
This JavaScript code snippet helps you to create draggable table rows on a webpage. It allows users to easily drag-and-drop sorting of table rows. It works by enabling you to click and drag table rows to rearrange their order. This functionality is helpful for creating interactive tables where users can easily reorder rows to suit their preferences.
How to Create Draggable Table Rows In JavaScript
1. Begin by creating an HTML structure for your table. Make sure to include the necessary HTML elements, like the <table>, <thead>, and <tbody>. For example:
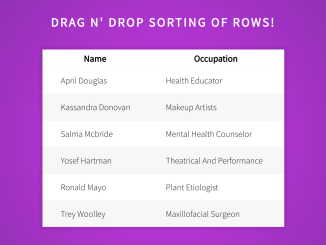
<p>Drag n' Drop sorting of rows!</p>
<table id="table" class="draggable-table">
<thead>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Occupation</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>April Douglas</td>
<td>Health Educator</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Salma Mcbride</td>
<td>Mental Health Counselor</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Kassandra Donovan</td>
<td>Makeup Artists</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Yosef Hartman</td>
<td>Theatrical and Performance</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Ronald Mayo</td>
<td>Plant Etiologist</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Trey Woolley</td>
<td>Maxillofacial Surgeon</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
Customize the table with your data by adding rows and columns within the <tbody>. You can insert additional <tr> elements with corresponding <td> elements inside the <tbody>.
2. Include the following CSS code in your HTML document to style the table and the draggable rows. This code will define the appearance of your table and the dragging effect:
* {
font-family: "Source Sans Pro", sans-serif;
}
body{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100vh;
background: #cb38e9;
position: relative;
background: radial-gradient(circle, #cb38e9 0%, #842fa8 100%) !important;
}
p {
font-size: 0.75em;
font-weight: bold;
position: absolute;
top: 15%;
width: 100%;
letter-spacing: 5px;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-align: center;
color: white;
user-select: none;
}
.draggable-table {
position: absolute;
top: 25%;
left: 20%;
width: 60%;
height: 50%;
border-collapse: collapse;
background: white;
-webkit-box-shadow: 0px 0px 10px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
box-shadow: 0px 0px 10px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
.draggable-table .draggable-table__drag {
font-size: 0.95em;
font-weight: lighter;
text-transform: capitalize;
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
text-indent: 50px;
border: 1px solid #f1f1f1;
z-index: 10;
cursor: grabbing;
-webkit-box-shadow: 2px 2px 3px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
box-shadow: 2px 2px 3px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);
opacity: 1;
}
.draggable-table thead th {
height: 25px;
font-weight: bold;
text-transform: capitalize;
padding: 10px;
user-select: none;
}
.draggable-table tbody tr {
cursor: grabbing;
}
.draggable-table tbody tr td {
font-size: 0.95em;
font-weight: lighter;
text-transform: capitalize;
text-indent: 50px;
padding: 10px;
user-select: none;
border-top: 1px solid whitesmoke;
}
.draggable-table tbody tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f7f7f7;
}
.draggable-table tbody tr:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: #ffffff;
}
.draggable-table tbody tr.is-dragging {
background: #f1c40f;
}
.draggable-table tbody tr.is-dragging td {
color: #ffe683;
}
3. Now, you’ll need to include the JavaScript code given. This code handles the logic for dragging and reordering the table rows. Place the following JavaScript code just before the closing </body> tag:
(function() {
"use strict";
const table = document.getElementById('table');
const tbody = table.querySelector('tbody');
var currRow = null,
dragElem = null,
mouseDownX = 0,
mouseDownY = 0,
mouseX = 0,
mouseY = 0,
mouseDrag = false;
function init() {
bindMouse();
}
function bindMouse() {
document.addEventListener('mousedown', (event) => {
if(event.button != 0) return true;
let target = getTargetRow(event.target);
if(target) {
currRow = target;
addDraggableRow(target);
currRow.classList.add('is-dragging');
let coords = getMouseCoords(event);
mouseDownX = coords.x;
mouseDownY = coords.y;
mouseDrag = true;
}
});
document.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => {
if(!mouseDrag) return;
let coords = getMouseCoords(event);
mouseX = coords.x - mouseDownX;
mouseY = coords.y - mouseDownY;
moveRow(mouseX, mouseY);
});
document.addEventListener('mouseup', (event) => {
if(!mouseDrag) return;
currRow.classList.remove('is-dragging');
table.removeChild(dragElem);
dragElem = null;
mouseDrag = false;
});
}
function swapRow(row, index) {
let currIndex = Array.from(tbody.children).indexOf(currRow),
row1 = currIndex > index ? currRow : row,
row2 = currIndex > index ? row : currRow;
tbody.insertBefore(row1, row2);
}
function moveRow(x, y) {
dragElem.style.transform = "translate3d(" + x + "px, " + y + "px, 0)";
let dPos = dragElem.getBoundingClientRect(),
currStartY = dPos.y, currEndY = currStartY + dPos.height,
rows = getRows();
for(var i = 0; i < rows.length; i++) {
let rowElem = rows[i],
rowSize = rowElem.getBoundingClientRect(),
rowStartY = rowSize.y, rowEndY = rowStartY + rowSize.height;
if(currRow !== rowElem && isIntersecting(currStartY, currEndY, rowStartY, rowEndY)) {
if(Math.abs(currStartY - rowStartY) < rowSize.height / 2)
swapRow(rowElem, i);
}
}
}
function addDraggableRow(target) {
dragElem = target.cloneNode(true);
dragElem.classList.add('draggable-table__drag');
dragElem.style.height = getStyle(target, 'height');
dragElem.style.background = getStyle(target, 'backgroundColor');
for(var i = 0; i < target.children.length; i++) {
let oldTD = target.children[i],
newTD = dragElem.children[i];
newTD.style.width = getStyle(oldTD, 'width');
newTD.style.height = getStyle(oldTD, 'height');
newTD.style.padding = getStyle(oldTD, 'padding');
newTD.style.margin = getStyle(oldTD, 'margin');
}
table.appendChild(dragElem);
let tPos = target.getBoundingClientRect(),
dPos = dragElem.getBoundingClientRect();
dragElem.style.bottom = ((dPos.y - tPos.y) - tPos.height) + "px";
dragElem.style.left = "-1px";
document.dispatchEvent(new MouseEvent('mousemove',
{ view: window, cancelable: true, bubbles: true }
));
}
function getRows() {
return table.querySelectorAll('tbody tr');
}
function getTargetRow(target) {
let elemName = target.tagName.toLowerCase();
if(elemName == 'tr') return target;
if(elemName == 'td') return target.closest('tr');
}
function getMouseCoords(event) {
return {
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
};
}
function getStyle(target, styleName) {
let compStyle = getComputedStyle(target),
style = compStyle[styleName];
return style ? style : null;
}
function isIntersecting(min0, max0, min1, max1) {
return Math.max(min0, max0) >= Math.min(min1, max1) &&
Math.min(min0, max0) <= Math.max(min1, max1);
}
init();
})();
That’s all! hopefully, you have successfully created an HTML table with draggable rows on your website. If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to comment below.
Similar Code Snippets:

I code and create web elements for amazing people around the world. I like work with new people. New people new Experiences.
I truly enjoy what I’m doing, which makes me more passionate about web development and coding. I am always ready to do challenging tasks whether it is about creating a custom CMS from scratch or customizing an existing system.



thanks for the tutorial, is there any way the table header can also be draggable like row but instead left or right
Hi Sohrab,
To make the table header draggable left or right similar to how rows are draggable up and down, you’d need to adjust the code. Here’s a modified version that adds the functionality to make the table header draggable horizontally:
function bindMouse() { document.addEventListener('mousedown', (event) => { // ... existing code ... else { let targetHeader = getTargetHeader(event.target); if (targetHeader) { currHeader = targetHeader; addDraggableHeader(targetHeader); currHeader.classList.add('is-dragging'); let coords = getMouseCoords(event); mouseDownX = coords.x; mouseDownY = coords.y; mouseDrag = true; } } }); document.addEventListener('mousemove', (event) => { if (!mouseDrag) return; let coords = getMouseCoords(event); mouseX = coords.x - mouseDownX; mouseY = coords.y - mouseDownY; // ... existing code ... else if (currHeader) { moveHeader(mouseX, 0); } }); document.addEventListener('mouseup', (event) => { if (!mouseDrag) return; // ... existing code ... else if (currHeader) { currHeader.classList.remove('is-dragging'); table.removeChild(dragElem); currHeader = null; } dragElem = null; mouseDrag = false; }); } function moveHeader(x, y) { dragElem.style.transform = "translate3d(" + x + "px, " + y + "px, 0)"; } function addDraggableHeader(target) { dragElem = target.cloneNode(true); dragElem.classList.add('draggable-table__drag'); dragElem.style.width = getStyle(target, 'width'); dragElem.style.background = getStyle(target, 'backgroundColor'); table.appendChild(dragElem); let tPos = target.getBoundingClientRect(), dPos = dragElem.getBoundingClientRect(); dragElem.style.left = ((dPos.x - tPos.x) - tPos.width) + "px"; dragElem.style.top = "-1px"; document.dispatchEvent(new MouseEvent('mousemove', { view: window, cancelable: true, bubbles: true })); } function getTargetHeader(target) { let elemName = target.tagName.toLowerCase(); if (elemName === 'th') return target; if (elemName === 'td') return target.closest('th'); }These changes modify the event listeners to handle table headers (<th> elements) as draggable elements and adjust their position horizontally (moveHeader function). The addDraggableHeader function creates a clone of the header being dragged and handles its placement. Also, the getTargetHeader function identifies the target table header.